Agriculture in Argentina is one of the main economic activities. Not only supplies the country but the surplus is exported. Argentina has a continental area of about 2.8 million square kilometers and around 37.5 million hectares of crops. Argentina’s main crops cultivated in this area are soybeans, wheat, corn, sunflowers, sorghum, and barley.
This article offers a general overview of the agricultural sector in 2024, relevant data on the main crops in Argentina, the magnitude of the areas planted by type of crop, main agricultural producing provinces, and the map of crops in Argentina by climatic zones.
CONTENTS
Important Facts about Agriculture in Argentina and its Position in the World
What are the main crops in Argentina?
The 6 main crops in Argentina are Soybeans, Corn, Wheat, Sunflower, Barley, and Sorghum. Total grain production in 2023/24 could reach 137 Mt, 65% more than the total volume obtained in the previous campaign and the 2nd best harvest since 2018/19
What is the crop production area in Argentina?
What are the main agricultural-producing provinces of Argentina?
Buenos Aires, Córdoba, and Santa Fe: they concentrate 75.84% of the surface destined for the production of oilseeds, and they add up to 72.7% of the implanted area that corresponds to cereals.
Mendoza, Tucumán, and San Juan: the three provinces, in decreasing order, add up to 58% of the fruit-planted area.
Salta, Córdoba, and Santiago del Estero: stand out in the cultivation of legumes, in decreasing order. The three main legume-producing provinces concentrate 77% of legume production:
How are crops distributed in the Argentine territory by climate areas?
The agricultural activity takes place in three zones temperate, subtropical, and arid; which are differentiated by their climatic conditions and aptitude for agriculture. The different soils and climates of the country offer a diversity of agricultural productions, adapted to the possibilities of each region.
See more
What are the agricultural products that are most exported in Argentina?
1st world exporter, of soy flour and oil, peanut oil and manufacturing, lemon juice and essential oil, organic fresh fruit to the EU, yerba mate.
2nd world exporter of fresh lemons and must
3rd world exporter of soybeans, corn, garlic, oils and fats, flour and sunflower oil
4th world exporter of olive oil
5th world exporter of wheat, raw peanuts
8th world exporter of sunflower seeds
10th world exporter of wine
What is the position of Argentina’s agricultural production in the world?
2nd world producer of yerba mate and 1st country with the largest harvested area of yerba mate
3rd world producer of soybeans and soybean meal
4th world producer of corn, producer, and processor of soybean oil and biodiesel based on soybean oil, seed, and sunflower oil
5th world producer of wine
7th world producer of oils and fats, boxed peanuts
8th world producer of citrus fruits
9th world producer of wheat
What are the main agricultural-producing provinces in Argentina?
Buenos Aires, Córdoba, and Santa Fe:
Concentrate 75.84% of the area destined for the production of oilseeds, and account for 72.7% of the planted area that corresponds to cereals.
Mendoza, Tucumán, and San Juan:
In descending order, these three provinces, account for 58% of the planted fruit area.
Salta, Córdoba, and Santiago del Estero:
They stand out in the cultivation of legumes, concentrating 77% of legume production
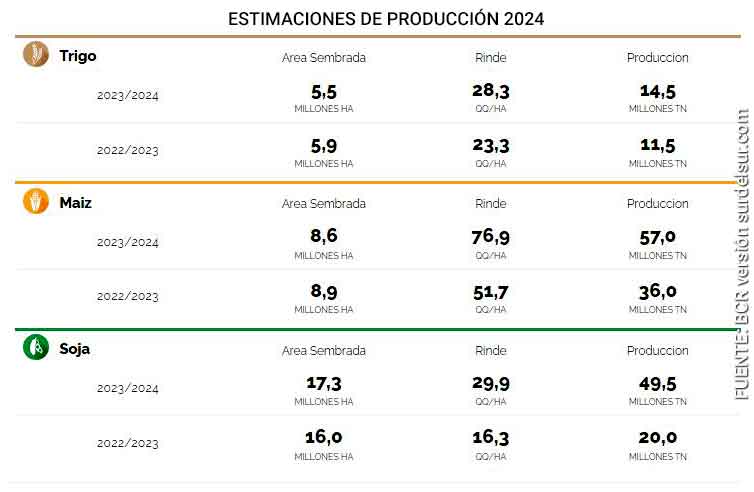
6 Main Crops by Production and Area
The 6 main crops: soybeans, wheat, corn, sunflowers, sorghum, and barley; with the production data in millions of tons and the planted areas in millions of hectares below
Main Crops Production and Area 2023/2024

SOYBEAN
17,3 MHa
49,5 MTn

CORN
8,6 MHa
57,0 MTn

WHEAT
5,5 MHa
14,5 MTn

SUNFLOWER
1,9 MHa
4,3 MTn

BARLEY
1,6 MHa
4,9 MTn

SORGHUM
0,95 MHa
2,4 MTn
In this way, total grain production in 2023/24 could reach 137 Mt, 65% more than the total volume obtained in the previous campaign. If this figure is confirmed, it would be the second-largest production in history, only behind the 140 Mt of the 2018/19 cycle.
Source: Mercado de Granos 2024 BCR
Production of the 3 main cereals: wheat, corn, and soybeans 2023/2024 compared to 2022/2023
According to the production estimates of wheat, corn, and soybeans, for the 2023/2024 campaign (Source BCR), values higher than those of 2022/2023 would be indicated for wheat, corn, and soybeans.
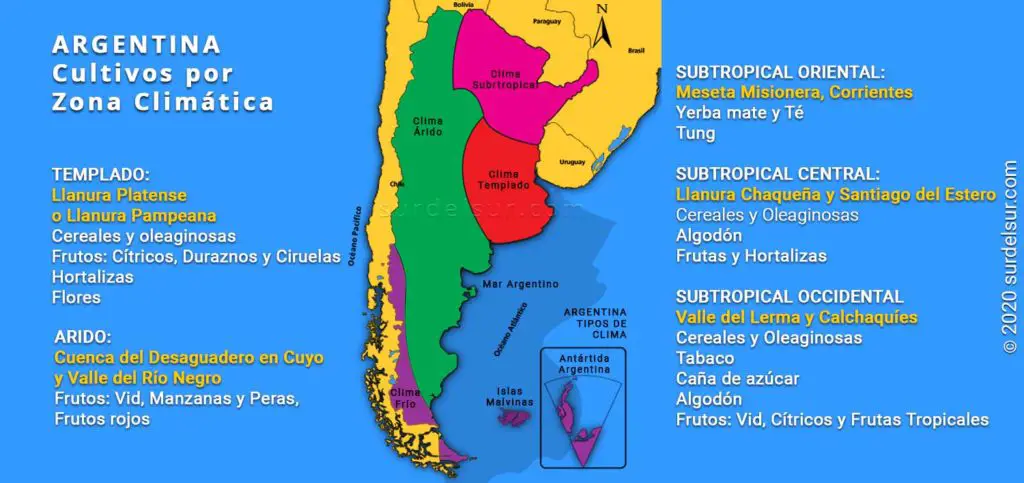
Argentina Agricultural Crop by Climate Areas
Main crops, production areas distributed in the Argentine territory by climate, and agricultural-producing provinces are important facts in Argentina’s agriculture.
Map of Argentina crops by climatic zone
Below we present on the map the information on the geographical distribution of agricultural production according to the climatic zone: temperate, subtropical, and arid zones. The infographic also indicates the different geographical regions of the country, which favor the agricultural production of different crops.
According to the prevailing climate, the country is divided into mild, sub-tropical, and arid regions. The different soils and climates in the country, offer a variety of agricultural products, adapted to the possibilities of each region.
Read more about Argentina’s Climate Types >>
1- Argentina Agriculture in Mild Climate Area

The temperate zone is formed by the Platense Plain or Pampean Plain southern part. Its plain relief, the fertility of its soil, its surface, and its mild climate, makes this region one of the best in the world for agricultural activity.
Cereals such as wheat with extraordinary yields are grown in the southeast of the province of Buenos Aires; and vegetables, among which the Balcarce potato stands out, also in Buenos Aires province. Fruits such as citrus, peaches, and plums are the favorites in the Rosario and San Pedro areas of Santa Fe province. Meanwhile, in Entre Ríos, mandarins, oranges, and lemons stand out. 50% of the total Argentine flower production is concentrated in the province of Buenos Aires.
2- Argentina Agriculture in Sub-tropical climate area

The subtropical zone is divided into eastern, central, and western.
- Crops in the eastern subtropical zone: Located in the northeast of Argentina, are the Misiones plateau and the province of Corrientes where yerba mate, tung, and tea are harvested. Tung is an oilseed native to Asia that has adapted well to this region and is used for polishing wood.
- Crops in the central subtropical zone: It is located in the center and north of Argentina, it is integrated by the Chaco plain. More than 80% of the national cotton production is harvested in Santiago del Estero, where, fruits and vegetables are also grown.
- Crops in the western subtropical zone: Located northwest of the Argentine territory. In this region, in the area of the Lerma Valley, cereals, tobacco, sugar cane, soybeans, and cotton are collected. On the other hand, the Calchaquíes valleys, stand out for their vines that produce exquisite wines. Also, the valley produces citrus and tropical fruits. Finally, we have the production of lemons in Tucumán, considered one of the most important in the country.
3- Argentina Agriculture in Arid Climate Area

The arid zone occupies 75% of the territory of Argentina. Agricultural activity in this area, given the scarcity of rainfall, places where it is possible to use the water rivers for irrigation.
This is the case of the Cuenca del Desaguadero in Cuyo, where the vine for wine production and table grapes, occupies most of the cultivated area in Mendoza, San Juan, and La Rioja.
In extra-Andean Patagonia, the Alto Valle del Río Negro stands out, dedicated to agricultural activity with the cultivation of apples and pears and their agro-industrial application.
List of types of crops in Argentina
According to the last National Agricultural Census, the types of crops are:
- Oilseeds
- Cereals
- Foragers
- Implanted forest and mountains
- Industrial crops
- Fruit trees
- Legumes
- Vegetables
- Aromatic, medicinal, and condiments
- Nurseries
- Cut flowers
To know the description of each of the different types of crops, their characteristics, in which province they are grown, the importance of production in Argentina, and the place in the world market of each product, consult the following report:
What types of crops does Argentina produce >>
WAS THE ARTICLE USEFUL TO YOU? SAVE IT!!
READ THE RELATED ARTICLE…!