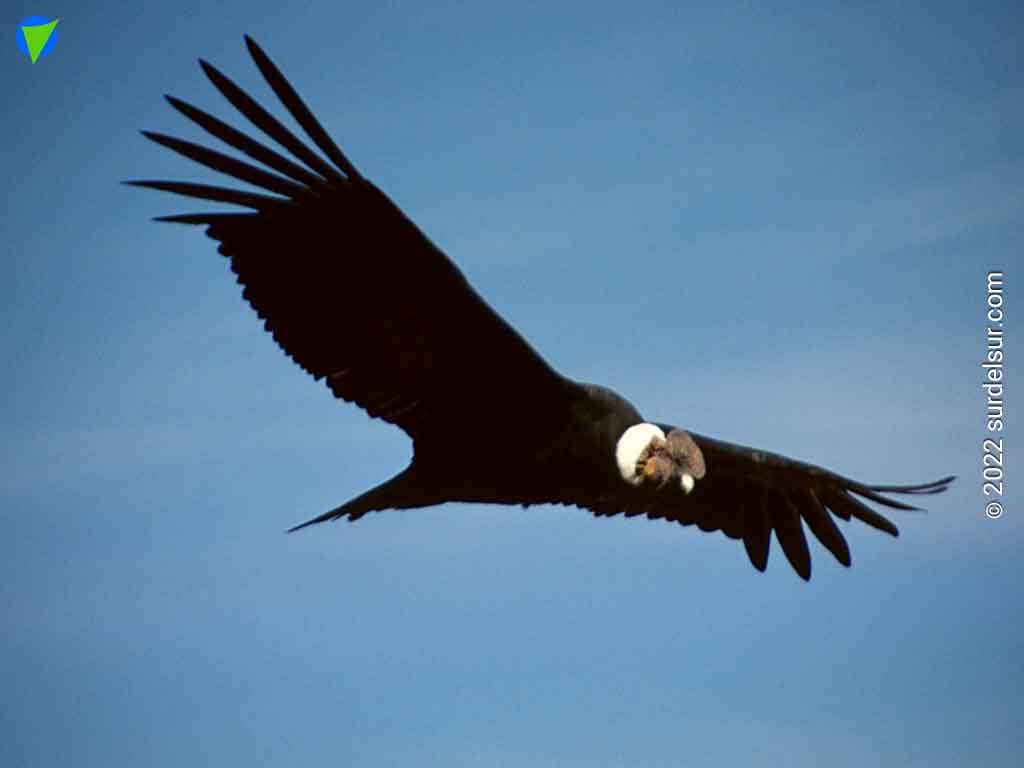
The Andean condor is the largest soaring bird in the world. With its 3.30 m (11ft) wingspan and 15 kg (33 pounds), the condor is the biggest size flying bird on Earth. This emblematic species lives in South America along the Andes Mountains. In Argentina, it is found in 14 of the 23 provinces. This important symbol of the Andean culture is currently in danger of extinction.
Although surpassed in wingspan by some albatross present in the South Atlantic, the condor, due to its enormous size and weight, is the largest among the flying birds on the planet.
In addition, the Andean condor is part of the Inca Trilogy: The condor, the puma, and the snake. Because it flew at a high altitude, above 5,000 meters, it was a sacred bird for the Incas, who believed in its ability to communicate the upper world with the earthly world.
What is the Andean condor like?
CLASSIFICATION:
- Class: Birds
- Subclass: Neornithes
- Order: Falconiformes
- Family: Cathartidae
- Scientific name: Vultur gryphus
- Common name: Andean condor
DESCRIPTION:
- Length: 3 to 4 ft. from head to tail.
- Wingspan (distance from one wingtip to the other): 10 ft or more.
- Weight: Generally around 25.5 pounds and can reach 33 pounds.
- Coloration:
- Adults (male and female): Reddish neck. In its lower part, there is a white down collar. The plumage is black, except on the back of the wings where it is white.
- Juveniles: Ochraceous brown throughout their plumage.
- Reproduction: Sexual maturity and reproductive behavior begins at five or six years of age and pairs for life. The reproduction rate is low, laying one or two eggs. It lives in mountainous terrain. Lays one white egg, measuring approximately 4 x 3 inches
- Average life: 70 years
- Food: Scavenger bird
- Sexual dimorphism:
- Males are larger than females, have a crest on their heads, and have brown irises.
- Females do not have a crest and the iris is red.
- Area Distribution: It inhabits South America along the Andes Mountains from Venezuela to southern Argentina.
CHARACTERISTICS:
- Head and neck: devoid of feathers, which facilitates cleaning after eating.
- Beak: strong and sharp allows them to open the toughest hides that other scavengers could not break.
- Legs: they have four fingers, three large front fingers with blunt and slightly curved nails, and a fourth opposite finger that is out of the plane of the previous ones, and little developed.
- Large crop: located at the base of the neck, it can carry up to 4 kilos of food.
- Wings: very developed allows them a perfect glide with almost no loss of energy, taking advantage of ascending and dynamic air currents; they can glide for hours and travel great distances in search of dead animals.
Where does the condor live?
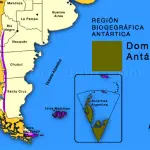
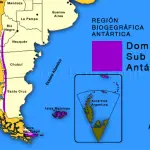
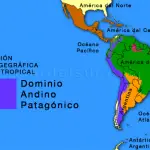
The condor inhabits South America along the Andes Mountains in Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina, which is called Andean Patagonian Domain. In our country, in the Andean mountainous area from north to south, it inhabits 14 Argentine provinces: Jujuy, Salta, Catamarca, Tucumán, La Rioja, and San Juan. Mendoza, Neuquén, Río Negro, Chubut, Santa Cruz, Tierra del Fuego and the Islands of the States. In the central zone of the country, the provinces of Córdoba, San Luis. The Andean condor prefers to nest and breed at altitudes of 3,000 to 5,000 masl. (9842 to 16400 ft) in rugged areas, specifically in large canyons, cliffs, and slopes.
What is the condor’s food?
It is a bird that feeds on carrion, so it plays an invaluable role in ecosystems. Look for all kinds of large dead animals, such as llamas, alpacas, deer, cows, etc. In its large crop, it can carry up to 4 kg. (8.82 pounds) of food, to feed its young.
How many kilometers can a condor fly?
The Andean Condor can fly for more than 5 hours and travel 170 km without flapping. It only flaps 1% of the time (Source: Institute for Research on Biodiversity and Environment INIBIOMA, CONICET-UNCOMA, and Swansea University, United Kingdom, Document). It glides in air currents, being able to reach more than 8000 m in height. When gliding, it keeps the wings spread horizontally and the primaries separated like fingers. It can move at speeds of up to 50 km/h. solitary or in groups.
Why is the condor endangered?
The Condor is in danger of extinction due to habitat loss and poisoning. The main cause of death is the ingestion of intoxicated or poisoned animals used as bait by hunters and ranchers. Ranchers use poisoned carrion to combat the attack of wild animals against livestock, such as foxes, pumas, and wild dogs. It was declared in danger of extinction and protected by National Law No. 22,421 (1981) for the Conservation of Wild Fauna. There is also a plan that promotes measures against the illegal use of toxic baits in the country (National Strategy against the Use of Toxic Baits) implemented by the Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development together with the Bioandina Foundation.
Condor watching
Condor watching, combined with hiking and horseback riding, in the universe of spectacular places offered by the Sierra de Comechingones
Birds in Merlo San Luis
There are 200 species of birds in the area that goes from Merlo to Papagallos on the western margin of the Sierra de los Comechingones, called Costa Comechingones