One of the most salient features of the Argentine territory is its variety of climates. humid, dry, tropical heat or nival cold, through different kinds of mild climates. Nothing remains outside the possibilities offered by the types of climate in Argentina.
CONTENTS
What is the Climate of Argentina
Argentina is characterized by having all the climates: warm, temperate, arid, and cold with all its varieties. This is a consequence of the different geographical factors such as latitude, relief, and the influence of the sea. Of course, the climate is also determined by the different meteorological phenomena that affect the climate such as wind, tornadoes, frost, and hail. These factors determine the different types of climate in Argentina and its varieties.
The diverse geographical regions in Argentina, are a determining factor of the different types of climates. To learn more about the different regions, and the Argentine water systems see Argentina Geographic Regions and Hydrography in Argentina
Types of Climate in Argentina
The warm, temperate, arid, and cold climates of Argentina, with all their varieties, define climatic regions in the Argentine territory as indicated on the map.
Argentina climate map
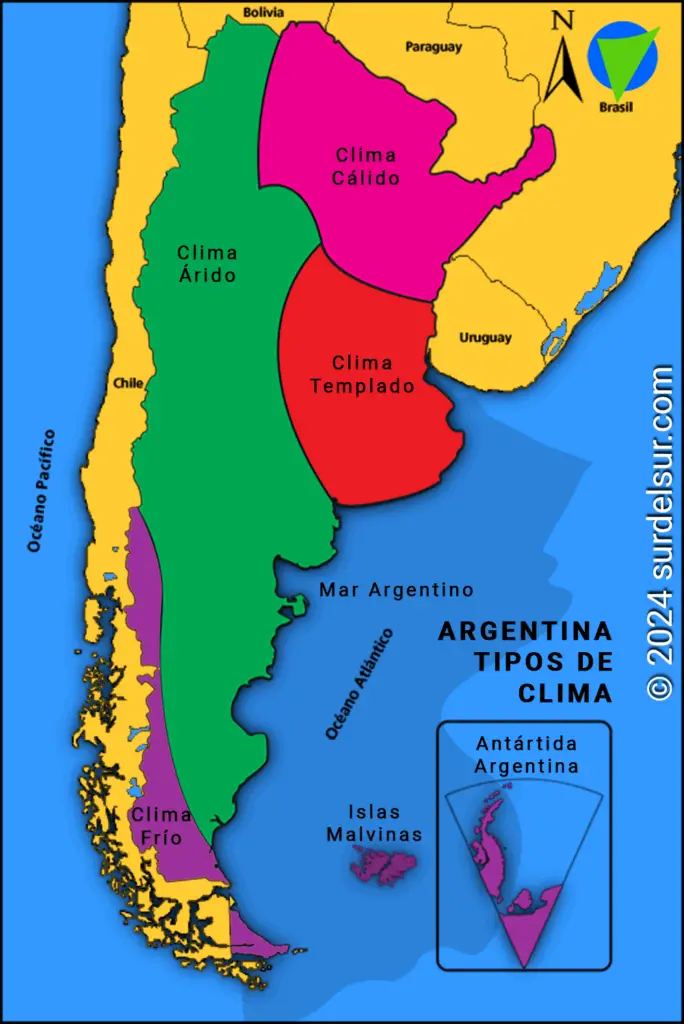
Types of climate and their varieties
The types of climate and their respective varieties are:
- Warm Climate
- Sub-tropical without a dry season
- Sub-tropical with dry season
- Sub-tropical of the sierras
- Mild Climate
- Pampas or humid weather
- Temperate transition
- Arid Climate
- High-mountain arid
- Sierras-and-fields arid
- Steppe arid
- Cold arid
- Cold Climate
- Humid or oceanic cold
- Nival cold
Below is the description of each type of climate and their respective varieties.
Argentina’s Types of Climate and their Characteristics
Below are each of the 4 types of climates and their characteristics, their geographical location and the varieties that make them up.
Warm Climate
It is found in the north-eastern angle of Argentina. Due to the decrease of the oceanic influence towards the west and the modifications of the mountainous relief, there are three varieties of this kind of climate:
- Sub-tropical without a dry season
- Sub-tropical with dry season
- Sub-tropical of the sierras.
Mild Climate
The temperate climate is in a climatic region that is located in the central east of Argentina. The amount and distribution of rainfall determine two varieties of mild climate:
- To the east, pampas or humid weather with strong oceanic influence on the southeast coast of Buenos Aires,
- A strip west, temperate transition occurs, to the arid climate. The average temperature is 15 ° C.
Arid Climate
The arid climate forms a climatic region that extends diagonally from the north and the Andes Mountains to the northwest to the Patagonian coast. According to the altitude and latitude, this climate shows four varieties:
- Arid high mountain, with a temperature depending on altitude and a very wide thermal range.
- Arid Sierras and fields with an average temperature of about 64º F (18º C).
- Arid Steppe, with an average temperature of around 59º F (15º C) and presenting frequent frosts, which occur even in summer.
- Arid Cold, with an average temperature of about 50º F (10º C), a fairly wide thermal range, and frosts occurring the whole year.
To learn more about the territorial development of Argentina, the area, perimeter, end points, and limits, consult Dimensions of Argentina
Cold Climate
The cold climate climatic region lies on the Andes Mountains and extends southward, encompassing Tierra del Fuego and the South Atlantic Islands, as well as Antarctica. There are two kinds:
- The Humid, or oceanic cold, with an average temperature of around 45º F (7º C), which can vary with height.
- The Snowy cold is characterized by permafrost, rainfall exceeding 800 mm, and westerly winds. Snowy cold weather prevails in Antarctica.
Geographical Factors Determining Climate
Due to its vast territory, Argentina presents a remarkable climatic diversity. In this sense, various geographic factors have a direct bearing, on determining the climatic characteristics of the different regions.
Influence of Latitude on the Climate of Argentina
Latitude is the distance from a given point on Earth to the equator. The warm areas are close to the equator, and the cold areas are far away from it. Therefore, latitude is one of the factors that affect the variety of climates.
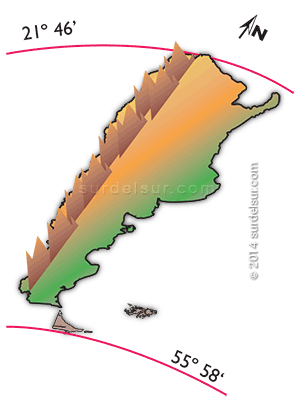
The Argentine Republic is characterized by a great latitudinal development, from 21º 46′ to 55º 58′ S. In other words, the territorial development of Argentina in a north-south direction along the 3,694 km., has consequently a great variety of climates. These climates range from tropical heat in the north to nival cold in the south.
Incidence of Relief on the Climate of Argentina
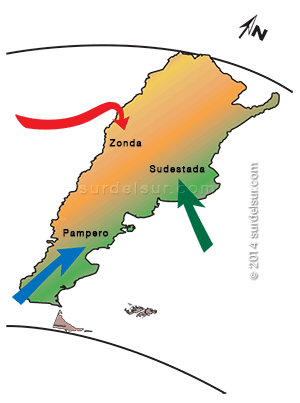
Certainly, the relief is a determining factor in the climate of Argentina. The great mountain ranges, especially the Cordillera de los Andes, extend from north to south, in western Argentina. This arrangement facilitates the circulation of air masses in the east of the country. Furthermore, relief influences temperatures insofar as the higher the altitude, the lower the temperature. This explains the presence of different winds: the Southwest, cold and dry; the Zonda, hot and dry; and the Sudestada, humid and cold.
Influence of Sea
The presence of the sea, which, in the case of the Argentine territory, constitutes a natural boundary to the east, exercises a moderating action, diminishing the thermal range.
The ocean brings its moisture to the continent through the winds. This phenomenon acts by moderating the climate, based on the ability of water to retain heat in the form of steam, producing warmer nights. That is, lower thermal amplitude. On the other hand, when the air humidity is low, the heat dissipates quickly, causing large differences in temperature between day and night, that is, a greater thermal amplitude.
Meteorological Factors influencing Climate
Winds
Different meteorological factors act on the Argentine territory, some of them are local, whereas the others originate beyond the Argentine boundaries, such is the case of the warm and humid winds coming from the Atlantic anticyclone and affecting the regions located to the north of Patagonia or the west winds coming from the Pacific anticyclone, as well as the cold winds from the Antarctic anticyclone.
These three winds permanently affect the Argentine climate, unlike the local winds, which include:
The Zonda: is warm and dry, generally blowing between May and October and originating to the east of the pre-cordillera in La Rioja, San Juan, and Mendoza.
The Sudestada: originates in the Pampa littoral and is characterized by its high humidity content.
The Pampero: coming from the south-west, is cold and dry, and blows mainly in summer, after several days of constant increase of temperature and humidity.
Tornadoes
Tornadoes consist of a mass of air in the shape of a vertical funnel, which reaches a rotating movement of up to 500 km/h and 250 meters in diameter. They originate between October and March in the Plata basin.
This area is called Pasillo de Tornados (Tornado Corridor), and it is the second most frequent area for tornadoes in the world, after the tornado region in the United States.
What is the Tornado Corridor? It is an extensive area in central Argentina, east of the Andes Mountains, where an explosive cocktail of cold, warm, and dry winds is created. As we said, in this region, the cold air masses of Patagonia and Antarctica converge; and the warm currents of northern Argentina, Paraguay, and Brazil; which is also added to the dry air of the Andes Mountains.
The collision between these different air masses that occurs in the Pampas Plain generates intense storms, hail falls, and tornadoes. The night of the 100 tornadoes, which paradoxically occurred on Tuesday, April 13, 1993, is memorable. This event was unique in the Argentine Republic and was studied for its exceptional nature by all meteorological services in the world.
Snowfalls
Because of the prevalence of mild weather in most of the territory and soon winter, snowfall is rare in most of the territory. They focus on intensity and frequency in the Andean sector.
Frost and Hail
Besides, there are also frequent snowfalls in the Andean area, as well as frosts (if only coincidentally with the advance of cold winds from the South Pacific or in high mountain areas and the Patagonian plateaus) and hail, which can fall in the whole territory, especially between September and December.
To see the weather forecast in Argentina at this time you can consult the Servicio Meteorológico Nacional. They also have an app. Pronóstico SMN Argentina for cell phones
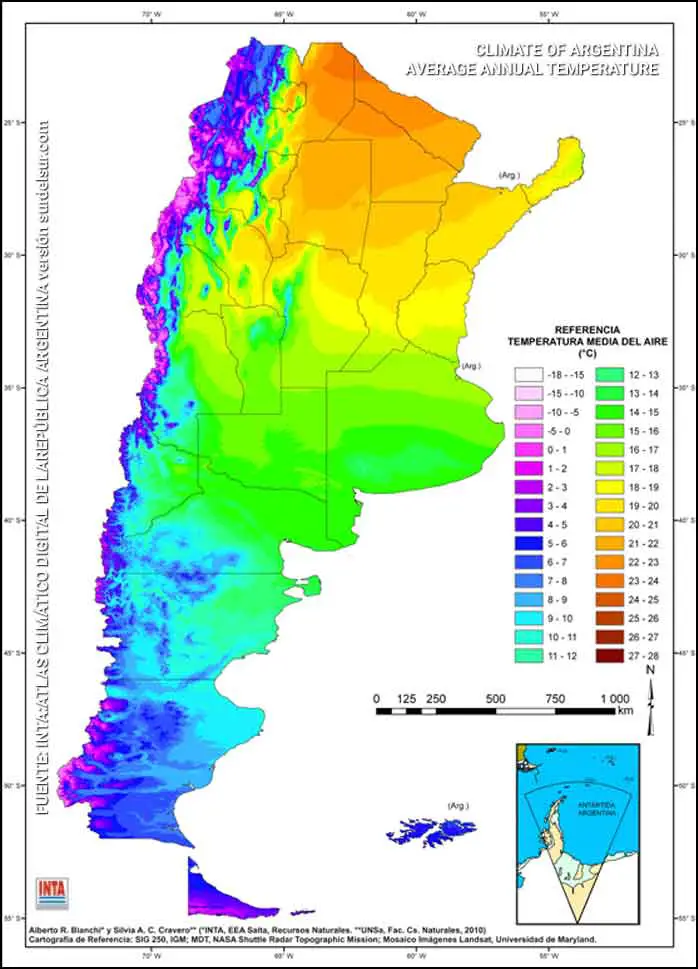
Argentina’s Annual Average Temperature
The average annual temperature in Argentina varies between 28°C (82,4°F) in the provinces of Salta and Formosa on the border with Paraguay and 5°C (41°F) in Tierra del Fuego.
Average Summer Temperature
Argentina is located in the south of South America, so the hottest month of the summer is January. Argentina’s average temperature recorded in the North is from 30 to 35 °C in the Chaco region. Meanwhile, in the South of Argentina, temperatures are between 8 and 10 °C in the province of Tierra del Fuego.
Average Winter Temperature
The coldest month of winter in Argentina is the month of July. Argentina’s average temperature in July is between 17°C in the North of the country and 0°C in Tierra del Fuego.
SOURCE: Atlas Climatico INTA
Servicio Meteorológico Nacional: Atlas Climático Argentina
WAS THE ARTICLE USEFUL TO YOU? SAVE IT!!
READ THE RELATED ARTICLE…!
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Bibliography
- National Meteorological Service Forecasts